New GST Rates Slash Prices of Daily Essentials From Today; Consumers to See Relief on Food, Hygiene Products

Starting September 22, 2025, the Indian government has implemented a major Goods and Services Tax (GST) overhaul aimed at simplifying the tax structure and providing relief to consumers on daily essentials. This historic GST reform collapses the previous multi-slab system into three main rates: 5% for essentials, 18% for most goods and services, and 40% for sin and luxury goods like tobacco and premium vehicles. With this change, households can expect lower prices on a wide range of food items, hygiene products, and packaged goods as companies pass on the tax benefits, providing welcome respite amid inflationary pressures.
What Changed: Simplifying GST Slabs on Essentials
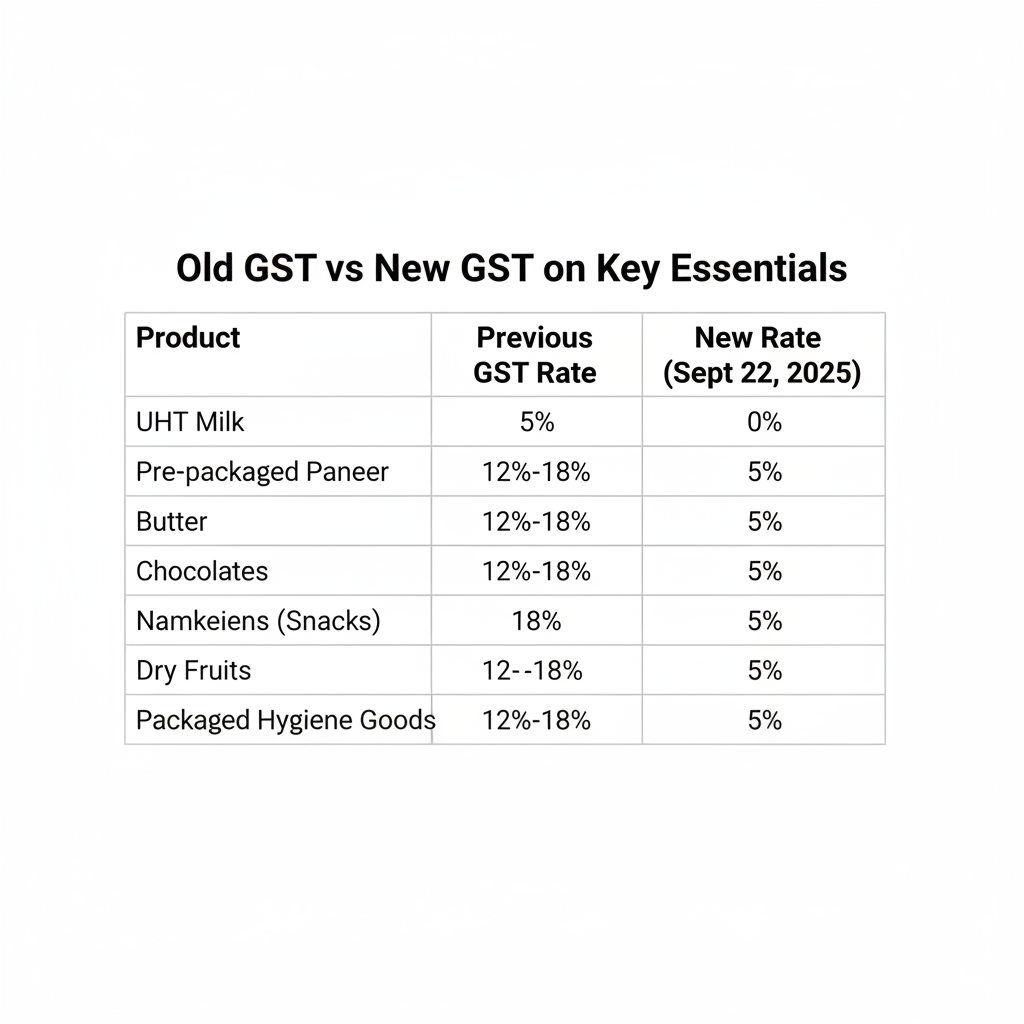
The GST reform replaces the prior four-tier tax rates of 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28% with a streamlined two-tier structure—5% and 18%—along with the new 40% slab for sin and luxury goods. Key daily essentials have moved mostly to the 5% slab, leading to significant tax rate cuts. Examples include staple foods such as UHT milk, pre-packaged paneer, roti, and bakery items that have shifted from 5% to zero or from 12%-18% to 5%. Dairy products like butter, ghee, cheese, and condensed milk now attract GST at 5% instead of 12%-18%. Popular grocery and snack items such as chocolates, pasta, namkeens, and dry fruits also benefit from reduced rates. Hygiene products and medicines are expected to be taxed at either 5% or exempt, simplifying compliance and lowering consumer costs. Full official rate lists released by the GST Council and Ministry of Finance disclose these changes as effective from today.
Consumer Impact: What Price Drops Mean for Households
For consumers, these rate cuts mean tangible price relief at supermarkets and local stores. The reduced GST on staples and packaged foods can translate into savings ranging from a few rupees to several tens of rupees per item depending on type and brand. A typical household buying a basket of essentials like milk, dairy spreads, bakery products, and snacks can expect monthly savings amounting to a few hundred rupees. This increase in purchasing power could encourage higher consumption and discretionary spending. Consumers should look out for updated price tags in stores to verify tax benefits and be aware that while most companies are expected to pass on these cuts fully, actual benefits could vary depending on supply chain pricing strategies. Overall, the GST cut acts as a direct stimulus for retail spending, which is particularly important given ongoing inflation concerns.
Business Impact: Adjusting to New GST Rates
FMCG companies and retailers have been preparing for this transition, revising price lists and recalibrating supply chains to reflect the simplified GST slabs. While some smaller traders may face short-term compliance challenges adjusting invoicing and accounting systems, overall the government has announced streamlined GST filing processes with faster refunds and pre-filled returns to ease the transition. For manufacturers, especially in dairy, packaged foods, and consumer goods sectors, the rate cuts reduce tax costs, improving competitiveness and margins. Retailers could leverage this reform by promoting affordable product lines and driving volume growth. However, companies need to carefully balance margin pressures with competitive pricing to retain market share while benefiting from likely higher consumer demand.
Inflation Context: RBI and Price Stability
The GST reform is designed to contribute to easing headline inflation by directly lowering tax-induced price components on frequently purchased goods. Given that retail inflation remains closely monitored by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), these rate cuts support the central bank’s inflation target and monetary policy stance. Reduced GST rates on essentials are expected to help moderate food inflation, a key constituent of the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This may reduce the pressure on RBI to hike rates further, potentially stabilizing borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. In this way, the GST reform dovetails with RBI’s ongoing efforts to balance growth and inflation control, fostering a more stable price environment.
Fiscal Implications: Revenue and Government Finances
While the rate cuts represent a deliberate reduction in GST revenue from lower tax rates on essentials, the government anticipates that enhanced consumption will partly offset revenue losses through volume growth. The new GST 2.0 framework also aims to broaden the tax base by easing compliance and formalizing more MSMEs and informal sector players under the tax net. The Finance Ministry and GST Council emphasize that these reforms balance revenue concerns with the need to support economic growth and consumer welfare. Notably, sin goods like tobacco and cigarettes maintain existing higher tax rates to protect revenue streams and public health priorities. Overall, the fiscal impact is expected to be manageable, with revenue losses spread across states but mitigated by economic expansion and streamlined tax administration.
Market Reactions: FMCG Stocks and Analyst Views
Equity markets reacted positively to news of the GST reforms, particularly boosting shares in FMCG companies expected to benefit from volume growth due to increased affordability. Analysts note that while margins might narrow slightly due to rate cuts, the expanded consumer base and faster turnover could enhance profitability. Consumer companies and market experts stress the importance of timely price adjustments by manufacturers to pass on tax benefits fully. Some caution that inflationary pressures on raw materials and supply chain costs remain risks. However, the overall market consensus appreciates the government’s effort to boost demand and simplify the indirect tax code, supporting sectors linked to household consumption.
Expert Commentary Placeholders
“Economic experts emphasize that the simplification of GST slabs will enhance transparency and ease of compliance, benefiting both consumers and businesses,” says [Economist’s Name], Senior Economist at [Institution]. “This reform reflects a targeted approach to empower households with more disposable income while supporting MSME growth.” [FMCG Analyst’s Name], Market Analyst at [Firm], adds, “The challenge for FMCG companies will be balancing margin pressures with capturing higher sales volumes as consumers respond to lower retail prices.” Trade expert [Expert Name] notes, “Retailers need to update pricing promptly and ensure consumers receive the full benefit of tax cuts to sustain trust during this transition.”
Quick Consumer Checklist
- Look for updated GST-inclusive price tags at retail outlets from September 22 onwards.
- Check receipts to confirm GST rates have been adjusted to 5% for applicable essentials.
- Expect price reductions mainly on packaged foods, dairy items, bakery products, and household hygiene goods.
- Be aware that while most businesses strive to pass on benefits, slight variations may occur; report discrepancies to consumer forums if needed.
Retail Watch: Household Monthly Savings
For an average Indian household spending approximately ₹3,000–₹4,000 per month on daily essentials covered by the new GST cuts, the reduction in tax rates could translate to monthly savings of ₹150 to ₹300. These savings add up over the year, providing households with increased disposable income for other expenses or savings. Retailers and local markets will display revised prices reflecting the new GST, making it easier for consumers to track benefits directly. This new GST regime provides tangible relief that should help ease the cost of living pressures, especially for middle and lower-income families.
Conclusion: Balanced Outlook for Consumers and Government
The new GST 2.0 reforms effective from today mark a landmark step in India’s tax policy landscape by simplifying rates and cutting taxes on essential goods. Consumers stand to gain through lower prices and improved affordability of critical food and hygiene products. Businesses benefit from streamlined compliance and potential demand boosts, though margin adjustments will require careful management. From a fiscal perspective, the reforms balance the immediate revenue trade-offs with long-term growth prospects and a more efficient tax system. Inflationary pressures may ease, supporting RBI’s efforts at price stability. The government’s challenge will be to ensure fair price pass-through by the industry and maintain robust revenue collections for developmental goals. Overall, households and investors can view these reforms as a positive catalyst for consumption-led growth and economic stability.
Summary to Easy Understand
India’s GST reforms introduce a simpler tax structure with two main slabs—5% on essential goods and 18% on most other items, plus a 40% slab for sin and luxury goods. Daily essentials like milk, paneer, butter, and packaged foods now attract lower GST rates, leading to expected consumer price reductions. The government aims to ease inflationary pressures and boost household spending with these rate cuts. Businesses are adjusting pricing and compliance processes, while the government balances revenue impact with growth objectives. Overall, consumers can anticipate meaningful savings and simpler tax administration starting today.