Sam Altman’s Predictions: AI to Automate Customer Support Jobs, Empathy-Driven Roles Stay Safe
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman predicts AI will soon replace many customer support jobs, while empathic careers like nursing remain secure due to human connection.
Altman’s Statement
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman recently stated in interviews including on The Tucker Carlson Show and during a Federal Reserve conference that AI will “totally, totally” automate large swathes of customer support positions. He described AI as a “super-smart, capable person” that can handle customer queries without transfers or errors, offering a faster, more consistent service than humans. Altman emphasized that when customers call for help, they will increasingly interact with AI rather than human agents. However, he also distinguished roles demanding empathy—such as nursing and caregiving—as unlikely to be replaced because these require deep human connection and emotional intelligence. Altman acknowledged uncertainty around programming jobs, noting AI is evolving productivity but also shifting software development roles in unpredictable ways. Altman framed the AI-driven job transformation as a fast-paced “punctuated equilibria” that compresses employment disruption historically spread over decades.
Which Jobs Are At Risk?
AI is set to disrupt phone- and computer-based customer support most directly. Jobs that involve repetitive clerical tasks, rule-based interactions, and basic data handling are particularly vulnerable. Examples include call center agents, help desk operators, data-entry clerks, and routine transaction processors. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can already manage 80–85% of internal customer queries at large tech firms. While currently there is some consumer preference for human agents, improving AI capabilities may shift this over time. Programming and software engineering face a complex future—AI boosts productivity but the impact on job volume remains unclear.
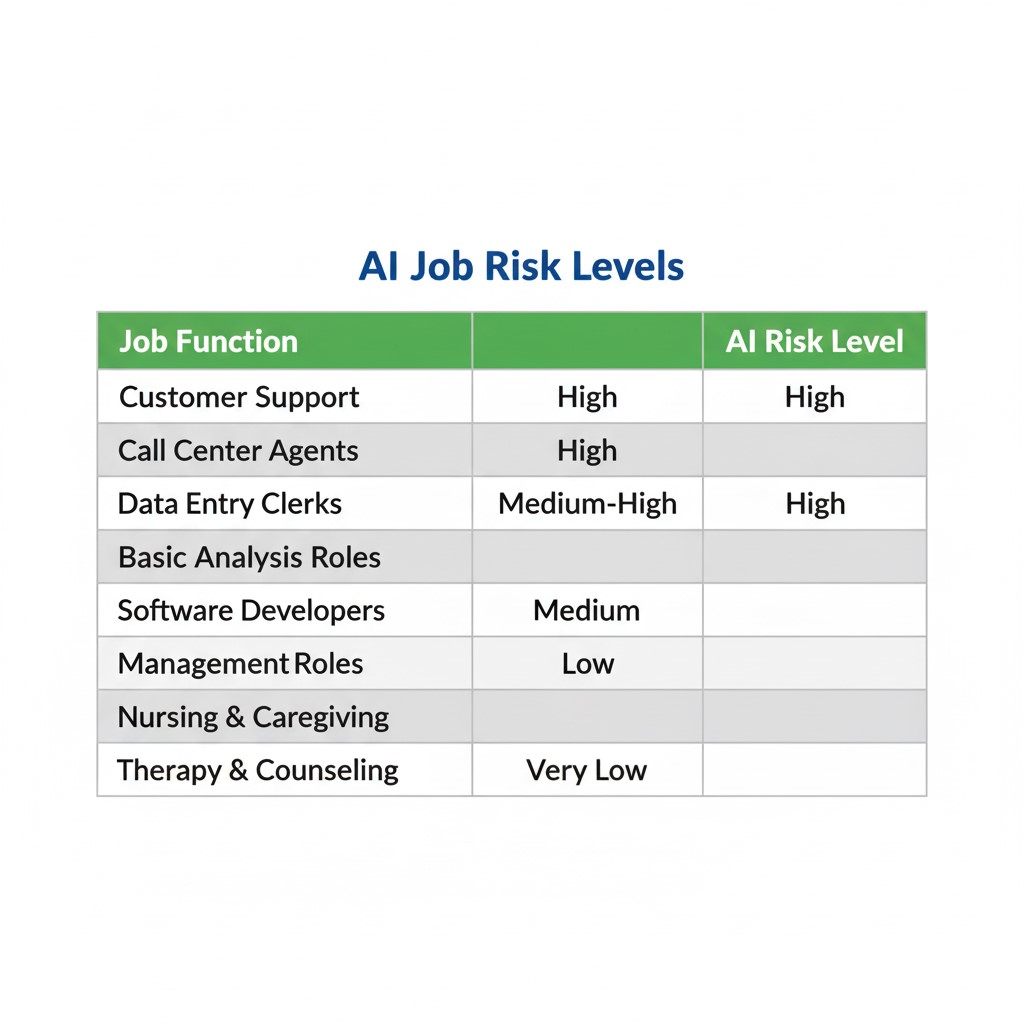
Why Empathy Matters
Jobs requiring empathy, emotional intelligence, and deep human contact—such as nursing, caregiving, therapy, and counseling—are significantly less automatable. AI systems lack genuine human connection, nuanced emotional understanding, and ethical judgment critical for these roles. Patients and clients often seek not just technical care but compassionate presence and support, which machines cannot replicate. This irreducible human element explains why empathetic professions remain secure amid rising AI penetration, reinforcing the value of skills centered around interpersonal relationships and human-centric services.
Economic Impact
In the short term, automation of customer support jobs could cause significant displacement in call centers and BPOs, sectors employing millions globally and notably in India. This raises concerns for workers dependent on such roles. Medium term benefits for businesses include substantial productivity gains and cost reductions; AI can handle queries error-free and instantly, reducing operational overheads. Long term, the labor market will likely shift with reskilling and job transitions, as new roles emerge managing AI systems or focusing on areas AI cannot penetrate, such as creativity, strategic decision-making, and human interaction.
India’s Context
India’s BPO and IT services sectors employ approximately 4.5 million people, many in customer support roles targeted by AI. NASSCOM reports show that about 35% of jobs in these sectors involve repetitive, rule-based tasks, making them AI-exposed. CMIE data reflect ongoing shifts with some workforce contraction in traditional roles but growth in digital and higher-value service jobs. The Indian government has prioritized skilling and reskilling initiatives—such as the National Skill Development Corporation’s programs—to enable workforce adaptation. However, high dependency on BPO incomes poses socioeconomic risks if automation advances faster than reskilling efforts.
Global Parallels
Markets in the US, EU, and Asia illustrate parallel trends. In the US, studies by McKinsey and the World Economic Forum suggest around 30% of current work activities could be automated by AI by 2030, with customer service among the top impacted areas. EU labor markets show cautious adjustment with policy focus on transition assistance. Asian economies, heavily invested in IT and BPO, also face workforce upheavals tempered by government-led upskilling. Global data underscore a mix of workforce disruption and opportunity as automation complements skill-augmented human workers.
Expert Commentary
“The rapid adoption of AI-driven automation in customer support is an inevitable step, but businesses must balance efficiency with customer experience,” said a Tech CEO.
“We foresee a significant labor market shift requiring proactive reskilling, especially in emerging AI management roles,” added an Economist.
“Healthcare jobs’ foundation in human empathy ensures their resilience, underscoring why care roles remain AI’s frontier,” noted a Healthcare Policy Expert.
Investor & Business Lens
Sectors poised to gain include AI software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms, automation tools, and customer experience optimization technologies. Conversely, sectors relying heavily on human empathy and complex judgment, such as healthcare and education, remain protected from wholesale automation. Investors would do well to monitor AI innovation leaders while businesses should strategize workforce transitions, balancing AI integration with human capital preservation.
Worker Takeaways
Workers should consider upskilling in AI literacy to manage, augment, or collaborate with AI systems. Emphasizing empathy, creativity, and hybrid roles blending technical and interpersonal skills will enhance job security. Embracing lifelong learning and flexibility will be critical as job scopes shift rapidly.
Sam Altman’s forecast spotlights AI’s transformative impact on jobs, sharply distinguishing functions susceptible to automation from those anchored in human empathy. His insights catalyze ongoing debates on balancing technological advancement, workforce transition, and social safeguards. For India and the world, the imperative is clear—prepare for AI’s fast-evolving role by embracing reskilling and valuing human-centric professions.








